GID-Iron and Steel
About GID-Iron and Steel Emission Database >
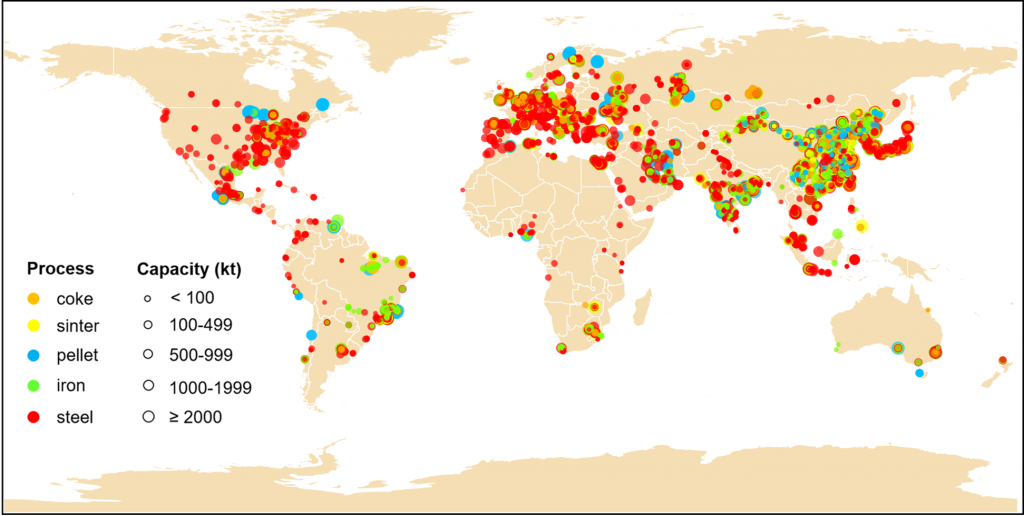
The GID-Iron and Steel Emission Database (GISD) provides CO2 and air pollutant emissions as well as underlying information of global multi-process iron and steel plants. GISD is based on the integration of global and regional iron and steel plant database such as the Metal Consulting International Limited (MCI) database created by James King (King, 2019). We compiled, combined, and harmonized the available data related to iron and steel production facilities including production of coke, sinter, pellet, iron (blast furnace, direct reduction and electric furnace), and crude steel (electric arc furnace, basic oxygen furnace, and open hearth furnace) from database described above, and filled data gaps with modelled emissions.
The GISD provides up-to-date elementary information and high-resolution emissions from global iron and steel plants, which includes plant-level, national, and regional capacity and age information, as well as anthropogenic emissions of CO2 and various air pollutants (SO2, NOx, primary PM, VOCs, CO, black carbon, and organic carbon). For elementary information which is obtained from collaborators’ database and restricted by user’s license (e.g., MCI), we provide cross-links to the original database. Users can purchase the relevant database and merge with GISD to get complete information at plant level.
Construction of the GID-Iron and Steel Emission Database >
The GISD is developed by using multisource data fusion technologies. The facility-level basic information of operating and retired coke ovens, sintering facilities, pelletizing facilities, ironmaking furnaces, and steelmaking furnaces is firstly compiled from the Metal Consulting International Limited (MCI) database for the historical time series, providing information on physical address, technology, capacity, start year of operation, retirement year, and relining/upgrading year of global facilities in iron and steel industry. Next, another database, the Global Steel Plant Tracker (GSPT) is integrated to supplement the missing information of global iron and steel production plants which is not contained in the MCI. Further, the GISD combines and harmonizes the more comprehensive and reliable data provided by official company websites. As for the geographical locations (exact latitudes and longitudes) of iron and steel production plants, they are obtained by using Google Maps to map the physical address provided in the MCI database and official websites of the companies. The GISD will be updated and improved as more and better data become available.
Estimates of facility-level emissions >
Facility-level information related to the estimates of CO2 and air pollutant emissions from above-mentioned global and regional datasets is integrated. In GISD, the estimates of emissions depend on modeled facility-level activity rates and emission factors. Facility-level activity rates are estimated by a function of facility capacity, energy efficiency, and capacity utilization rate, with the constraint of country-level production from the World Steel Association and fuel consumption from the International Energy Agency (IEA). CO2 emission factors are obtained from IEA, IPCC Guidelines, and previous literatures.
The GID team will timely update air pollutants and carbon dioxide emission inventory and continuously provide high-quality data products by integrating more high-resolution local datasets. If you are looking for more detailed emissions and potential collaboration, please contact us.
If you have any questions, please contact gid@tsinghua.edu.cn.
Related references:
King, J., Global iron and steel database, 2019, available from Metals Consulting International Limited (MCI, https://www.metalsconsultinginternational.com).
Global Energy Monitor, Global Steel Plant Tracker, 2022, available from https://globalenergymonitor.org/projects/global-steel-plant-tracker/
World Steel Association, Steel Statistical Yearbook, 1990-2020, available from https://www.worldsteel.org/steel-by-topic/statistics/steel-statistical-yearbook.html
International Energy Agency (IEA), World Energy Statistics and Balances 2021, available from https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-balances-overview
IPCC, 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, 2006, available from https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/
Development History >
The development of GID-Iron and Steel Emission Database started in 2020 and we will keep tracking and updating infrastructure changes and related emissions periodically.
- In February 2021, GISD v1.0 product is released. This online dataset provides basic information of global iron and steel infrastructure and related CO2 emissions in 2019 with different aggregated levels (global summary data for number of plants, total capacity and CO2 emissions, region-level and country-level data for capacity, age and CO2 emissions, and plant-level data). Emissions of air pollutants and emissions for other years will be available once they are finished.
- In September 2023, GISD v1.1 product is released. Now GISD v1.1 provides basic information and related CO2 emissions of global coking, sintering, pelletizing, ironmaking, and steelmaking facilities in 1990-2020 with different aggregated levels (global summary data for total capacity and CO2 emissions, region-level and country-level data for capacity, age and CO2 emissions, and plant-level data). Emissions of air pollutants for the corresponding years will be available once they are finished.
Readme >
- All GISD products are restricted to non-commercial purposes. Any uses of GISD products by business organizations are regarded as commercial purposes which need prior authorization.
- Any papers, reports or products using the GISD data should cite the related publications and GID website completely, please see HOW TO CITE.
How to cite >
Using GISD product should cite GID website (http://gidmodel.org.cn/) and the following paper:
Xu, R., D. Tong, S.J. Davis, X. Qin, J. Cheng, Q. Shi, Y. Liu, C. Chen, L. Yan, X. Yan, H. Wang, D. Zheng, K. He and Q. Zhang (2023), Plant-by-plant decarbonization strategies for global steel industry, Nat. Clim. Change, X, XX-XX.
Wang, X., Y. Lei, L. Yan, T. Liu, Q. Zhang and K. He (2019), A unit-based emission inventory of SO2, NOx and PM for the Chinese iron and steel industry from 2010 to 2015, Sci. Total Environ., 676, 18-30.
